CO2List.org
Information on Daily Sources of CO2
METRIC and US Measures
Quick Look at Some Data
To keep global warming under 2°, we have to keep CO2 under 2 tons (tonnes) per person per year worldwide. If you use more CO2 now, you need to use less later. We have global warming because the world now averages 6 tons of CO2 per person per year (US 22, China 4, India 1).
___________________________
Producing Each Line below Releases 1 Ton or Tonne of CO2
90 lb of red meat (cows' methane & growing grain), 41 kg
300 lb of chicken, fish or eggs, 155 kg
700 lb of cereal or carbohydrate, 300 kg
1,200 lb of fruit or vegetables, 550 kg
1,000 lb of paper or plastic, 400 kg
26 square feet of living & working space (building it), 2.4 sq.m
1 year of electricity (at 100 watts) from grid
100 square feet of solar collectors (300 watts on sunny days), 10 sq.m
20,000 gallons of hot water, 70,000 liters
700,000 disposable plastic bags, recycled
1,600 miles in a 28 mpg car, 2,600 km at 12 kpl (8l/100km)
1,600 passenger miles in a plane, 2,600 km
2,000 miles in a 40 mpg car, 3,200 km at 17 kpl (6l/100km)
3,000 passenger miles in a local bus, 4,600 km
3,000 miles walking (producing food; shoes, sidewalks), 4,700 km
5,000 passenger miles in a train, 8,500 km
8,000 miles bicycling (pedal or electric), 13,000 km
12,000 passenger miles in a long distance bus, 19,000 km
(These include making vehicle, road, rails, airports, etc.)
$1,700 spent in USA, overall average
$1,500 spent on construction in USA
$2,000 spent on hotels or restaurants in USA
$3,000 spent on education, health, telephone, internet in USA
$7,000 spent on computers in USA
Just a little meat, driving, flying, buying or construction creates a ton of CO2. Keep your eye on these; they are far more important than hot water, disposable plastic bags, or unplugging equipment.
CO2 to Produce Items (Metric)
22 kilos CO2 per kilo of red meat
5.9 kilos CO2 per kilo of chicken, fish or eggs
2.9 kilos CO2 per kilo of cereal or carbohydrate
1.7 kilos CO2 per kilo of fruit or vegetables
381 kilos CO2 per square meter, to build houses
225 kilos CO2 per square meter, to make solar cells
3.2 kilos CO2 per liter of heating oil
2.4 kilos CO2 per cubic meter of natural gas
0.8 kilos CO2 per kwh of electricity
0.5 kilos CO2 per dollar spent in the USA, average
0.47 kilos CO2 per passenger-km on flights of 800 or 13,400 km
0.35 kilos CO2 per passenger-km on flight of 1,300 km
0.37 kilos CO2 per passenger-km on cruise
0.34 kilos CO2 per kilometer in a 12 kpl (8l/100km) car
0.28 kilos CO2 per kilometer in a 17 kpl (6l/100km) car
0.11 kilos CO2 per passenger-km in a train
0.13 kilos CO2 per kilometer bicycling on bike lane
0.05 kilos CO2 per kilometer bicycling without bike lane
0.20 kilos CO2 per passenger-km in local bus
0.05 kilos CO2 per passenger-km in long distance bus
(These include making vehicle, road, rails, airports, etc.)
CO2 to Produce Items (Pound / Mile)
22 lb CO2 per lb of red meat
5.9 lb CO2 per lb of chicken, fish or eggs
2.9 lb CO2 per lb of cereal or carbohydrate
1.7 lb CO2 per lb of fruit or vegetables
78 lb CO2 per square foot, to build houses
46 lb CO2 per square foot, to make solar cells
27.0 lb CO2 per US gallon of heating oil
15.0 lb CO2 per therm or 100 cubic feet of natural gas
1.7 lb CO2 per kwh of electricity
1.2 lb CO2 per dollar spent in the USA, average
1.67 lb CO2 per passenger mile on flights of 500 or 8,300 miles
1.23 lb CO2 per passenger mile on flight of 2,500 miles
1.30 lb CO2 per passenger mile on cruise
1.20 lb CO2 per mile in a 28 mpg (US) car
1.00 lb CO2 per mile in a 40 mpg (US) car
0.38 lb CO2 per passenger mile in a train
0.45 lb CO2 per mile bicycling on bike lane
0.19 lb CO2 per mile bicycling without bike lane
0.71 lb CO2 per passenger mile in a local bus
0.17 lb CO2 per passenger mile in a long distance bus
(These include making vehicle, road, rails, airports, etc.)
.
US electricity fuels & prices by region & time of day
Newer source for building materials (EC3)
Law firms for fossil fuels
Or cooling in US southeast over 110 years: planting trees cools southeast
Warmer climate makes spring leaves appear on trees in NY 19 days sooner than 200 years ago.
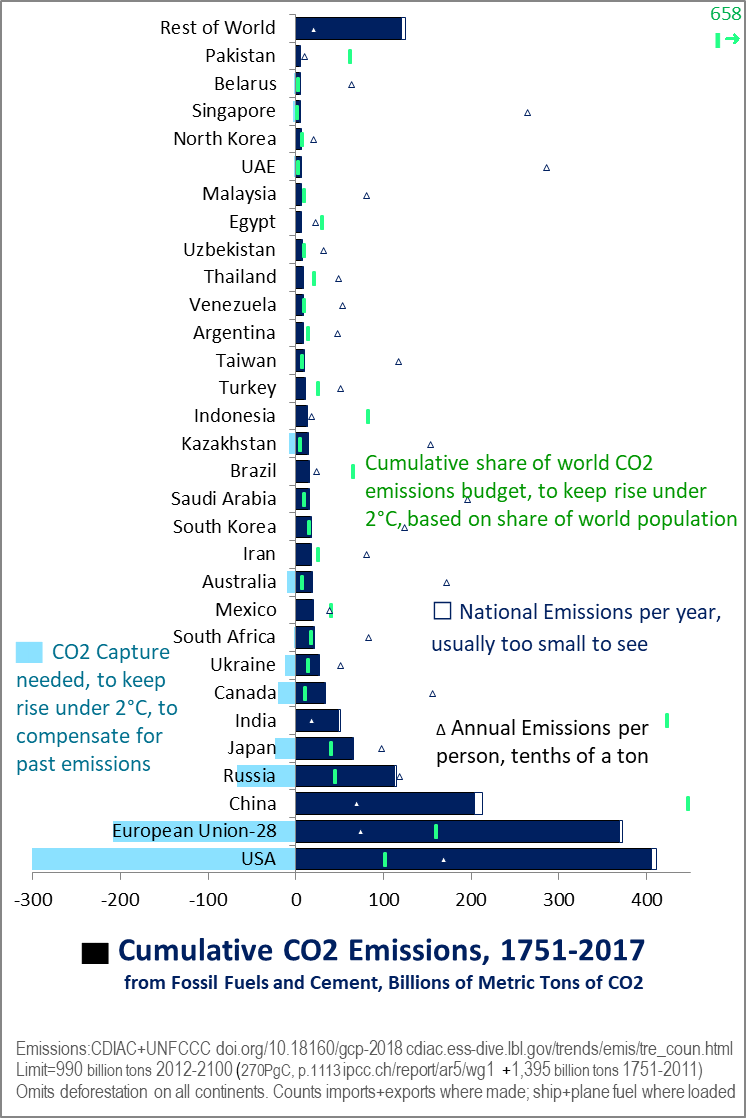
How much Carbon Dioxide can the world handle?
Can Wave energy provide power?
Emissions of different fuels with + without capture (xlsx)
Cars drive most efficiently at 46-53 miles per hour (75-85 kph), in order to do well on ratings from EPA in the US.
CO2 footprint calculators (Any country, metric and pound/mile)
Spreadsheet of products shows every step in our calculations, every source, and summaries for every country.
Use an easy climate model
__________________
About us & how to help this site
Email a friend about this site
Print a postcard
It has a short list of CO2 sources. Mail it or give it to people you know
Privacy policy